Marine Natural Hazards
The earthquakes in Indonesia in 2004 and Japan in 2011 with the subsequent tsunamis demonstrated the risks for population and infrastructure not only in coastal regions but also far beyond. In order to better assess natural hazards from the sea and protect ourselves, for example through early warning systems, we need to better understand the underlying processes and monitor the development of the sea floor closely.
mareXtreme: Innovative Approaches to dealing with Marine Natural Hazards
In the DAM research mission “Paths to improved risk management in the area of marine extreme events and natural hazards”, short title mareXtreme, from 2024 around 150 scientists from 29 partner organizations are researching how to deal with the interactions between short-term multiple and cascading extreme events and natural hazards and their long-term effects on marine ecosystems and social life on the coast.
The four joint projects ElbeXtreme, METAscales, MULTI-MAREX and PrimePrevention are investigating georisks as well as biological and oceanographic-meteorological risks. The projects ElbeXtreme and MULTI-MAREX are cooordinated at GEOMAR. The aim of mareXtreme is to significantly improve the ability to predict marine extreme events and natural hazards, to support the sustainable development of coastal communities and to strengthen the resilience of coastal societies.
More about the start of mareXtreme (GEOMAR News from 23.01.2024)
PRE-COLLAPSE: Landslides and Collapses on Marine Volcanic Flanks
Video in german with english subtitles
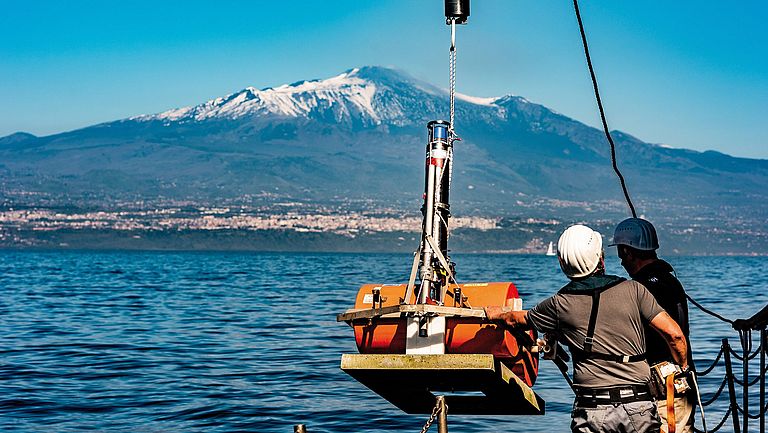
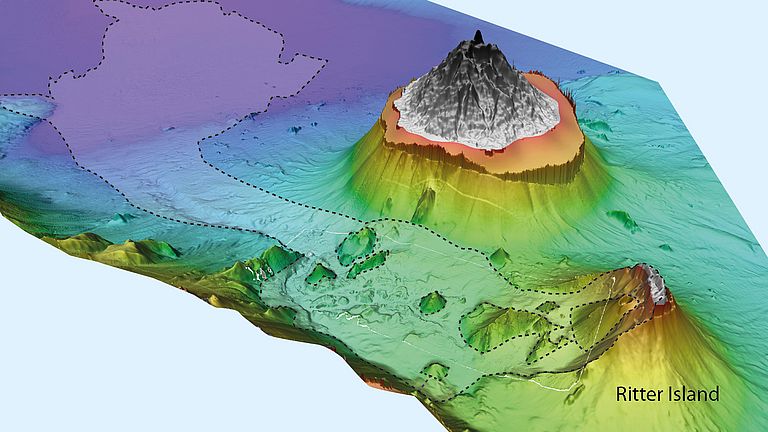
In 2018, researchers from Kiel were able to demonstrate for the first time that the eastern flank of Etna volcano, which descends into the Mediterranean Sea, is slowly moving downslope under water. These movements could be interpreted as an indication of an imminent collapse of the volcano's flank at some point in the future. Such a collapse would most likely result in a tsunami. But when exactly is there a danger of flank collapse? How can this danger be better estimated? Geoscientist Dr. Morelia Urlaub from GEOMAR is working on answering these questions. She received a prestigious Starting Grant from the European Research Council for her project PRE-COLLAPSE. PRE-COLLAPSE focuses on the volcanoes Etna (Italy), Anak Krakatau (Indonesia), Ritter Island (Papua New Guinea) and Kilauea (Hawaii, USA). On-site measurements, numerical models, and laboratory experiments on volcanic rocks will combine to provide new insights into what mechanisms trigger large flank collapses. The measuring instruments deployed on Etna in the fall of 2020 will also contribute important data to the project.
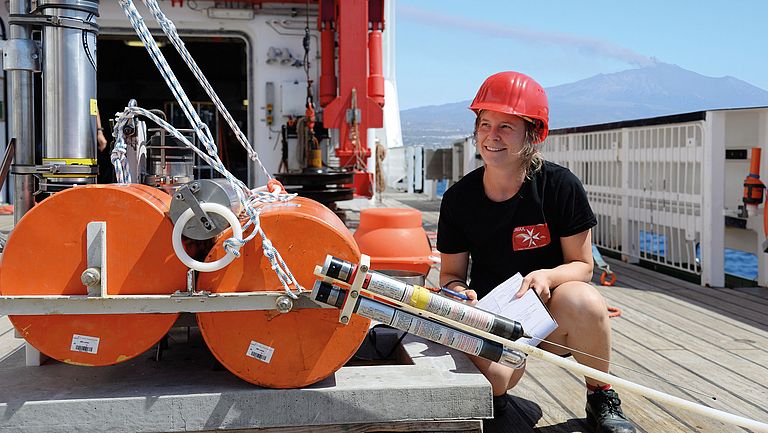
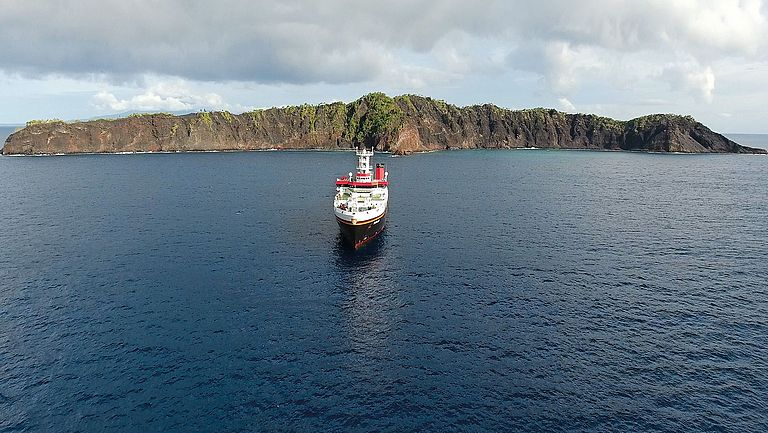
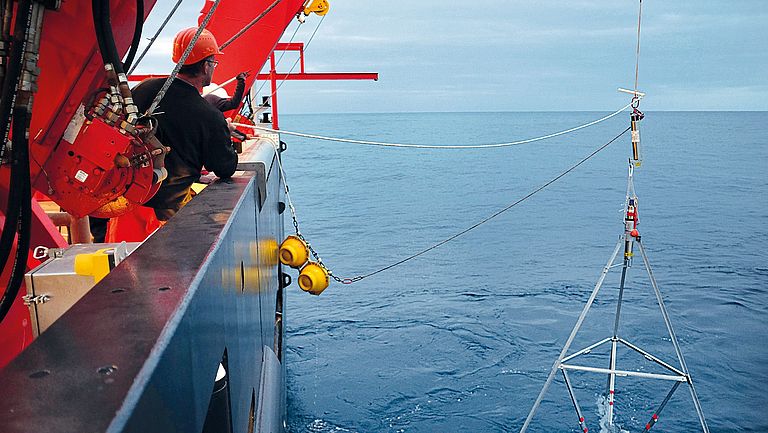
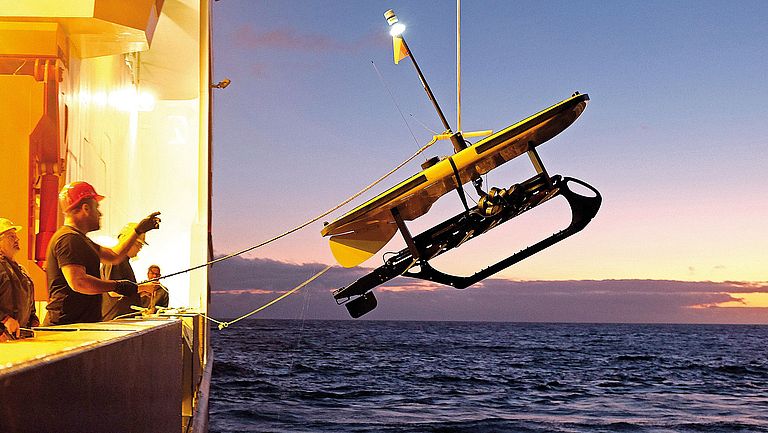
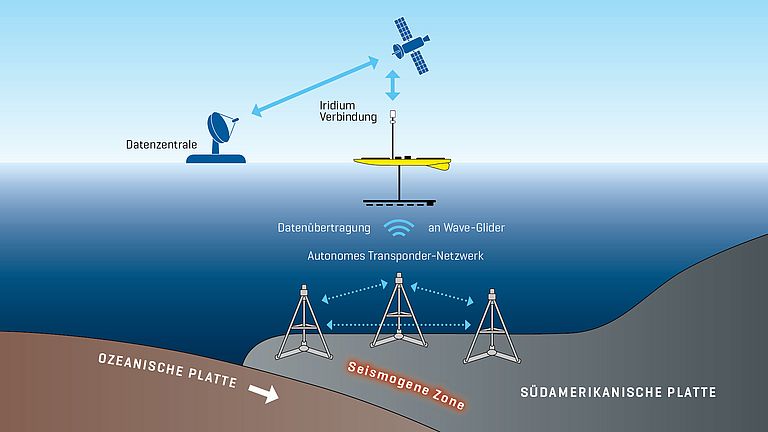
GeoSEA: A new Geodetic Monitoring Network off the Coast of Northern Chile
Video in german
The coast off Chile is a highly earthquake-prone region, where an oceanic earth plate dips below the South American continent and tectonic stresses build up in the process. To record these and better assess the risk of strong earthquakes, the geodetic network GeoSEA was installed off northern Chile in 2015 on expedition SO244 with the German research vessel SONNE. GeoSEA is a mobile autonomous network of seafloor stations to record active deformations of the seafloor. Just over six years after deployment, GeoSEA has now been recovered as part of SONNE expedition SO288. The findings will contribute to a better understanding of geological risks in the region and to the further development of seafloor observation systems.










![[Translate to English:] Drawing of a submarine cable, also showing the fibres inside the cable](/fileadmin/_processed_/a/4/csm_AdobeStock_263883542_4340636663.jpeg)






![[Translate to English:] A small platform with orange-coloured cylinders splashes onto the surface of the sea](/fileadmin/_processed_/9/8/csm_151208_1345_0746_SO244_JSteffen-GEOMAR_994a48f076.jpg)

![[Translate to English:] Kernthema Gefahren und Nutzen des Meeresbodens: Wie können wir marine Naturgefahren frühzeitig erkennen und Ressourcen vom Meeresboden verantwortungsvoll nutzen?](/fileadmin/_processed_/0/5/csm_teaser_gefahren_ressourcen_2021_572726b0a8.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] Visual PoF Topic 3 Ruhelose Erde](/fileadmin/_processed_/f/4/csm_t3_teaser_7cbc913ec4.jpg)


